MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER
Miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is an automatically operated electrical switch is used to interrupt the circuit under fault conditions such as overload and short circuit.
It was invented by Mr. Stotz-Kontakt in 1891.
MCB does not interrupt the circuit under the earth fault condition.
CONSTRUCTION
There are basically four types of MCB,s such as:-
1. Single-pole MCB 2. Two-pole MCB
3. Three-pole MCB 4. Four-pole MCB
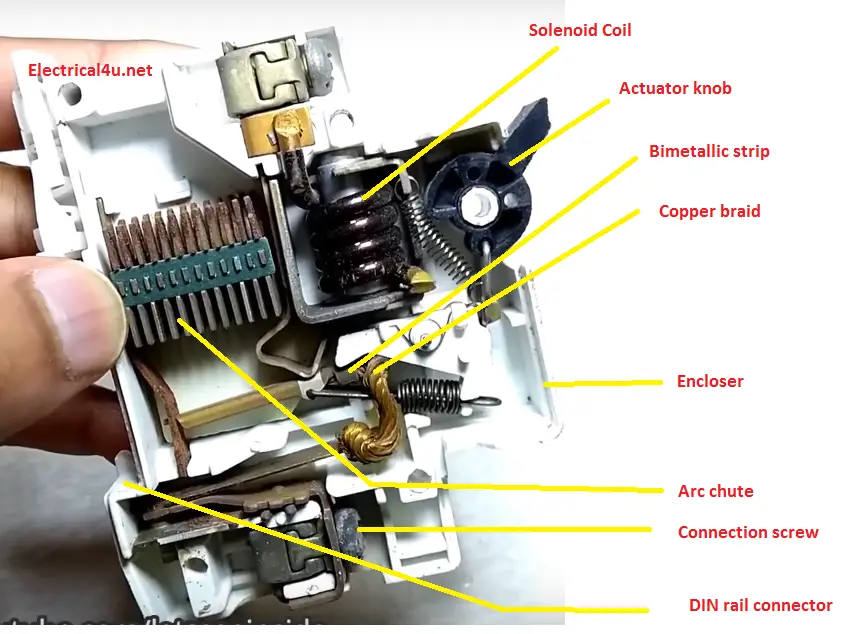
Actuator knob:
It involves turning on and off operation of the MCB. This is the only mechanism used to indicate the status of the miniature circuit breaker. If the knob is in the upward direction, it is considered as ON position, if it is in a downward position,it is considered as off position.
Solenoid/magnetic trip coil:
It is a coil used to trip the circuit breaker under short circuit and instantaneous fault condition. It is connected in series with the inIput line.The inner part of the coil consists of a tripping rod, plunger, and a return spring.
Bimetallic strip:
- A bimetallic strip is a small connecting metal that is associated with the tripping mechanism. It is a combination of steel and copper or steel and brass. Mostly steel is used since the resistivity of the steel is high.
- The bimetallic arrangement is used to trip the circuit under an overload condition. It works based on “the physical state of the metal changes when the temperature of increase”.
Arc chute:
Arc chute is a bunch of steel plates with zinc-coated material arranged. The main purpose of the arc chute is quenching the arc which developed inside of the MCB while breaking the circuit.
Connection screw:
An electrolytic copper or steel screw allows us to connect the MCB to the power source. Mostly the bottom and top side screw indicate the output and input terminal.
Copper braid:
It is used to connect the moving element to the standstill element.
DIN rail connector:
The DIN rail connection is used to mount an MCB in a rack.
Encloser:
All the operations are performed inside of the encloser and which is riveted to get better mechanical strength. The encloser is made up of high insulated fiberglass.
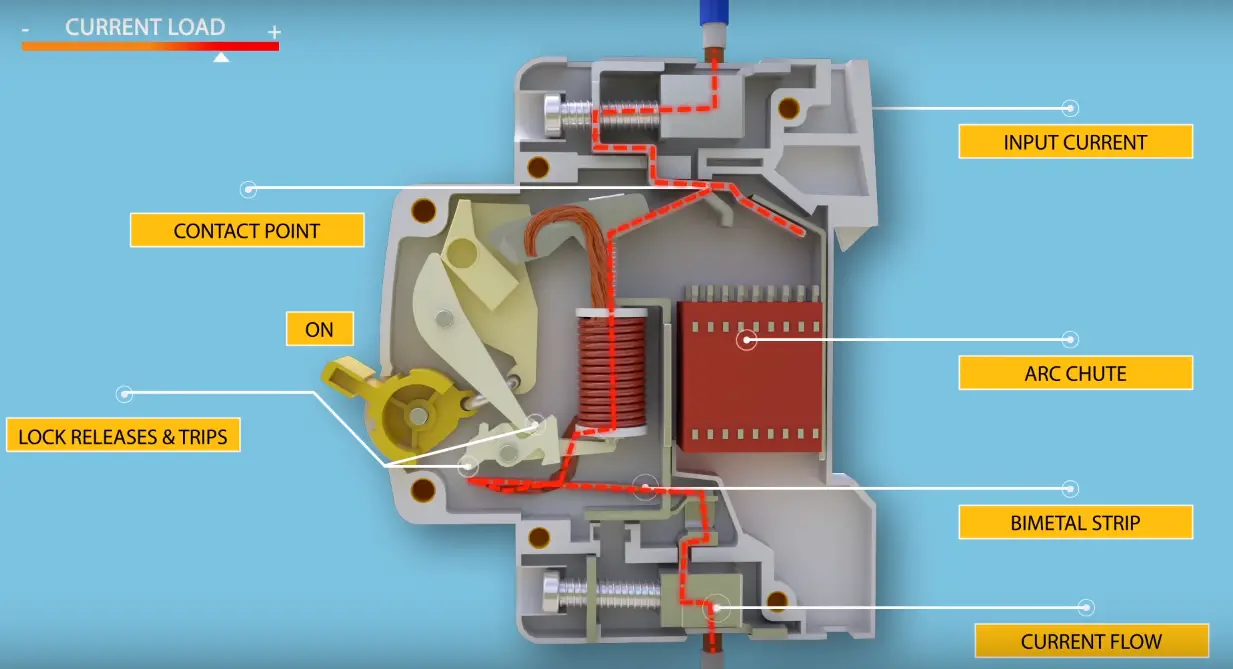
WORKING
The circuit breaker mainly operates during short circuits and overloads.
- The overhead protection is achieved by a bimetallic strip when the overload occurs the bimetallic strip becomes heat and starts to deflect or bend. In doing so, it releases the latch mechanism and causes the contact to open.
- Whereas, the short circuit protection is given by the solenoid coil. On the occurrence of a short circuit, the short circuit current energizes the solenoid coil, thus the coil operates the plunger to move and to strike the trip lever which causes an immediate release of the latch mechanism.
- The operating time of a miniature circuit breaker is less than 5 milliseconds. The miniature circuit breakers are available with different ratings such as 5, 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, etc.
- The arc chutes are used to vanish the arc produced in the circuit breaker while interrupting the circuit.
Types of MCB on the basis of Tripping Characteristics
The tripping current and operating time of each MCB types are given in the table below.
| Type | Tripping Current | Operating Time |
| Type B | 3 To 5 times the full load current | 0.04 To 13 Sec |
| Type C | 5 To 10 times the full load current | 0.04 To 5 Sec |
| Type D | 10 To 20 times the full load current | 0.04 To 3 Sec |
| Type K | 8 To 12 times the full load current | <0.1 Sec |
| Type Z | 2 To 3 times the full load current | <0.1 Sec |
No comments:
Post a Comment